How to Create a Cross-Platform IoT Mobile App
Table of Contents
Lauch your IoT product in few weeks for MVP
Learn more
Understanding Cross-Platform IoT Mobile Applications
A cross platform IoT app lets users control and monitor connected devices from iOS and Android using a single codebase. Think smart thermostats, wearables, factory sensors, EV chargers, or industrial gateways—all producing data and exposing controls that your app visualizes and orchestrates in real time.
At its core, an IoT mobile experience bridges four layers: devices and sensors, connectivity and protocols, cloud or edge services, and the mobile client. The mobile layer authenticates users, discovers devices, subscribes to telemetry (e.g., via MQTT), sends commands, and renders insights. This demands careful attention to iot mobile app architecture: topic hierarchies or REST endpoints, device identity, state synchronization, offline-first behavior, and secure session management.
Why cross-platform? Faster delivery, a unified roadmap, and shared UI logic. With tools like React Native and Flutter, teams can ship native-feel experiences, while reusing business logic and protocol integrations. The result: faster MVPs, consistent iot app ui ux design, and lower maintenance.
Typical use cases:
- Smart home and consumer electronics (lights, plugs, cameras)
- Industrial IoT (condition monitoring, predictive maintenance)
- Healthcare wearables and remote patient monitoring
- Energy and EV charging networks
If you’re evaluating verticals, explore smart homes for consumer-centric UX and industrial IoT for robust telemetry and alerts. See: Smart Home Automation App Development and Industrial IoT: Building Remote Monitoring Systems.
SEO tip: target phrases like cross platform iot app, react native iot app, flutter iot app development, iot mobile app architecture, and iot app ui ux design across headings and content to improve discoverability.
Defining Project Requirements for Your Cross-Platform IoT App
Start with clarity. A well-defined scope prevents rework and accelerates delivery.
Key questions:
- Business objectives: What outcomes matter most—engagement, device sales, reduced downtime, subscription revenue?
- Users and contexts: Who are your personas (technicians, homeowners, operators)? What environments (factory floors, homes, vehicles)?
- Devices and capabilities: What sensors/actuators? Which connectivity types (Wi‑Fi, BLE, cellular)? Do you need provisioning, firmware updates, or scenes/automation?
- Platforms and hardware: iOS and Android versions, flagship vs. low-end devices, tablets, wearables.
- Data: Telemetry frequency, historical retention, dashboards, alerts, and edge processing.
- Security and compliance: Encryption, authentication, PII handling, data residency, audit trails.
Prioritize features in milestones. MVP might include login, device pairing, status, basic controls, and alerts. Phase 2 can add automation rules, OTA updates, and advanced analytics.
Budget and timeline: Hardware pilots, certifications, and QA across device matrices can impact costs. For detailed planning, see the guide: IoT App Development Cost: Complete Guide.
Industry fit: Requirements vary by vertical. For industrial remote monitoring (high reliability, alerting, offline workflows), review: Industrial IoT: Building Remote Monitoring Systems. For consumer-focused comfort and scenes, explore: Smart Home Automation App Development.
Deliverables checklist:
- PRD with clear user stories and acceptance criteria
- Device inventory and protocol matrix
- Architecture outline (mobile, cloud, data, security)
- Non-functional targets (latency, battery, availability)
- Compliance requirements (GDPR/CCPA, SOC 2, sector-specific)
Choosing the Right Framework: React Native vs Flutter vs Alternatives
Framework choice shapes development speed, runtime performance, and integration complexity.
Quick take:
- React Native is a strong default for a react native iot app if your team knows JavaScript/TypeScript and you need flexible native integrations (Bluetooth, networking, background services).
- Flutter iot app development offers excellent performance, a cohesive UI system, and predictable rendering across platforms.
- Xamarin/.NET MAUI and Ionic can be viable given team expertise and app requirements.
Comparison table:
| Framework | Language | Performance & UI | IoT Integrations | Ecosystem | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| React Native | JavaScript/TypeScript | Native components; good performance with modern architecture (Fabric, TurboModules) | Mature BLE/Wi‑Fi, MQTT via native or JS libs; strong native module story | Large community | Teams with web/React skills; rapid iteration; complex native integrations |
| Flutter | Dart | High FPS, consistent across devices; rich custom UI | BLE, sockets, MQTT via plugins; method channels for native | Fast-growing | Pixel-perfect UI, smooth animations, multi-platform targets |
| .NET (Xamarin/MAUI) | C# | Native bindings; good performance | Access to native APIs; enterprise-friendly | Microsoft ecosystem | .NET-heavy orgs; enterprise integration |
| Ionic/Capacitor | JS/TS + Web | Web-based UI; acceptable for many apps | Plugins for BLE/Wi‑Fi; may need native plugins | Web dev friendly | Content-driven UIs; hybrid apps with moderate device control |
Practical tips:
- For a react native iot app: use the new architecture for lower bridge overhead; prefer native modules for latency-sensitive BLE operations; enable Hermes for lower memory.
- For flutter iot app development: leverage isolates for parsing or compression; prefer platform channels for time-critical device SDKs; use const widgets and Rive/Lottie carefully to manage jank.
- Prototype early: Validate device pairing flows, background tasks, push notifications, and offline storage in a thin spike before fully committing.
Ecosystem planning: Pair your framework with a robust IoT platform and database strategy. Explore: Top 10 IoT Platforms You Should Use in 2025 and Choosing the Right Database for IoT Applications.
Decision heuristic:
- If your team is JS-heavy and you need fast shipping plus native control, choose React Native.
- If you want a unified rendering engine and rich custom UI with predictable performance, choose Flutter.
- If you are invested in .NET, consider MAUI/Xamarin for a tighter C# stack.
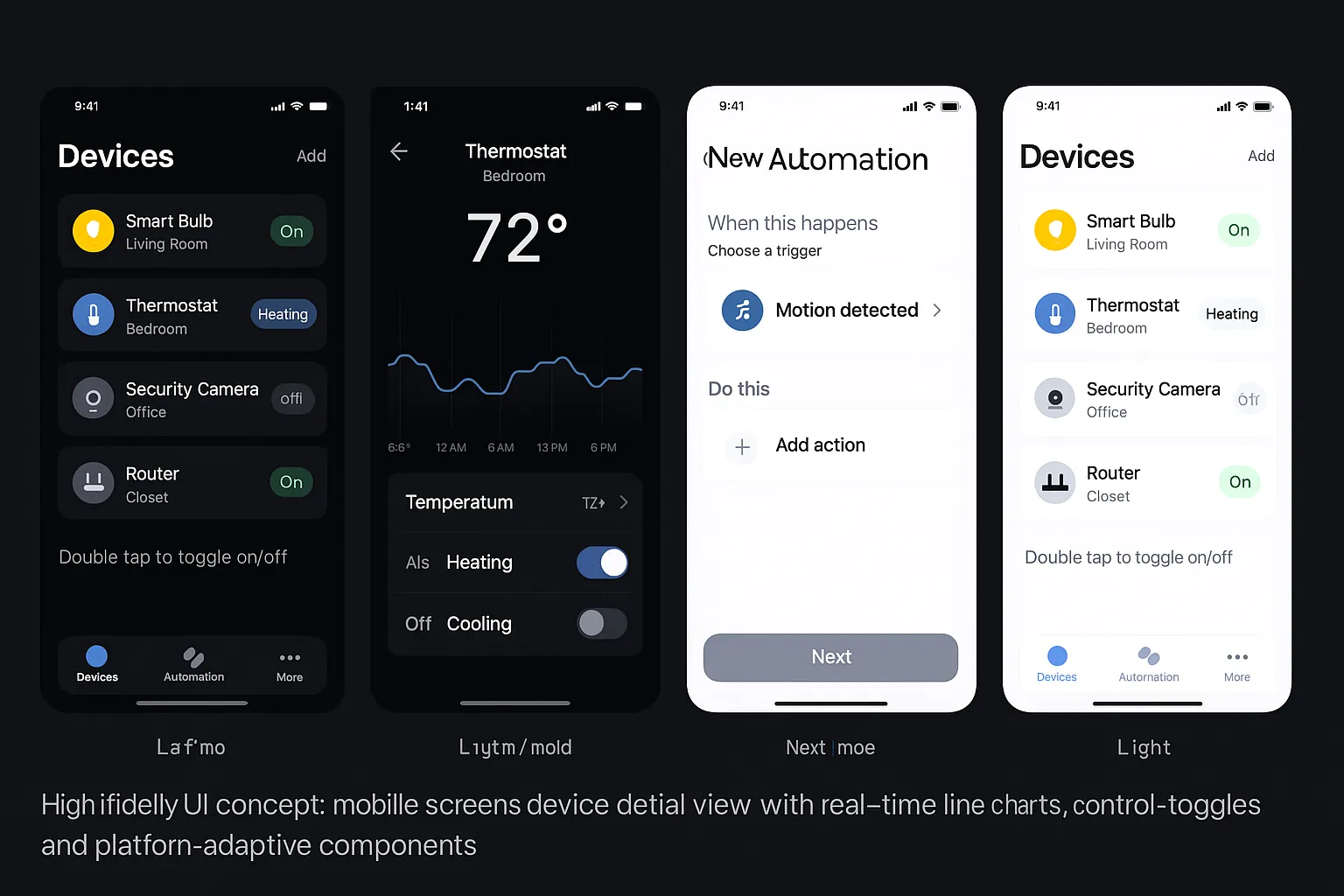
IoT App UI/UX Design: From Device States to Dashboards
Great iot app ui ux design balances clarity, responsiveness, and error resilience—across iOS and Android.
Principles:
- Device-first mental model: Make primary device actions one-tap accessible. Show live status and allow quick toggles.
- Statefulness and feedback: Represent states like online/offline, syncing, updating firmware, or degraded connectivity. Use color and iconography consistently.
- Progressive disclosure: Keep key controls on top; tuck advanced settings under details.
- Real-time visuals: Use sparklines, trend chips, and compact charts for telemetry at-a-glance.
- Offline-first: Queue commands with clear status; reconcile when online.
- Accessibility: Support large text, VoiceOver/TalkBack, high-contrast and motion-reduced UIs.
- Error recovery: Provide actionable errors and retry paths; log error context for support.
UI patterns that work:
- Home: device cards with critical KPIs; bulk actions and scenes.
- Device detail: timeline of events, charts, and control panel.
- Alerts: inbox with severity filters and snooze.
- Automation: rule builder (if-this-then-that) with preview and conflict checks.
Framework notes:
- React Native: reuse cross-platform components, leverage native gestures and bottom sheets.
- Flutter: use custom theming and adaptive widgets for platform nuances.
Design resources: For dashboards and data storytelling patterns, see How to Build an IoT Dashboard. For consumer flows like scenes and schedules, explore Smart Home Automation App Development.
SEO tip: Include target phrases like iot app ui ux design and cross platform iot app in H2/H3s and image alt text.
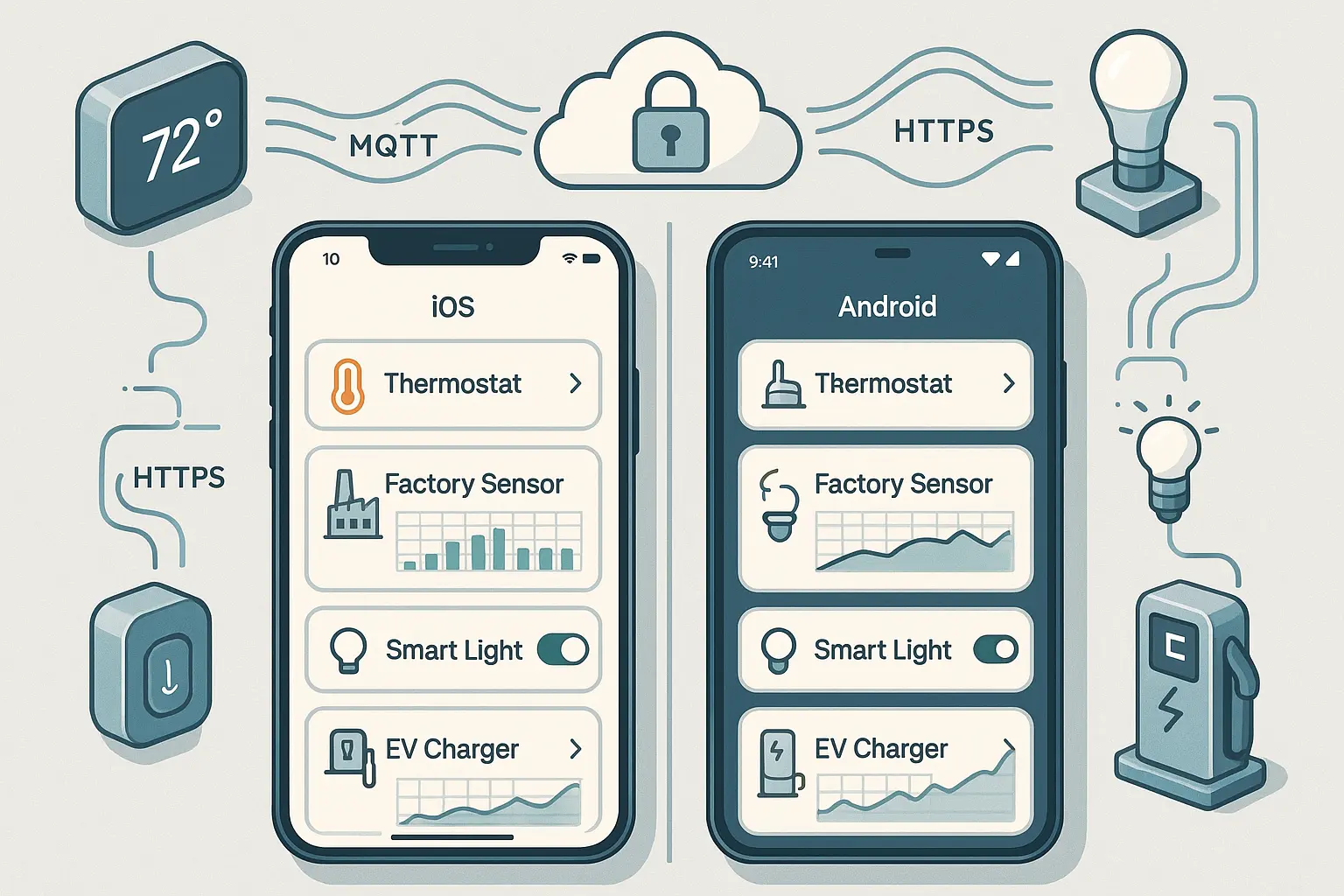
Implementing Device Communication Protocols
Communication choices shape reliability, latency, battery usage, and complexity. Pick protocols based on constraints and device capabilities.
Common options:
- MQTT: Lightweight pub/sub ideal for IoT. Low overhead, great for real-time updates and unreliable networks. Use QoS levels and retained messages wisely.
- HTTPS/REST: Standard, firewall-friendly, ideal for configuration and less time-sensitive telemetry.
- WebSockets: Persistent, full-duplex; good for server-to-app push without MQTT.
- BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy): Local provisioning and control; pair phones with nearby devices and then bootstrap Wi‑Fi credentials.
Quick comparison:
| Protocol | Best Use | Pros | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MQTT | Live telemetry, commands | Low bandwidth, QoS, retained messages | Requires broker, topic design, security hardening |
| HTTPS/REST | Config, infrequent reads | Simple, widely supported | Higher overhead, polling unless using SSE |
| WebSockets | Bi-directional push | Real-time without broker | Keepalive and reconnection logic |
| BLE | Provisioning, local control | No internet needed, low power | Limited range, platform BLE APIs complexity |
Best practices:
- Model topics/endpoints around device identity and capabilities.
- Implement reconnection with exponential backoff, jitter, and offline queues.
- Prefer push over polling; compress payloads; batch telemetry.
- Test under network constraints (2G/3G, high latency, packet loss).
Integration tips:
- React Native: use native BLE modules for reliable scanning and bonding; consider native MQTT clients for performance.
- Flutter: validate plugin maturity on your target OS versions; test background execution and reconnection thoroughly.
Architectural fit: Your protocol layer ties directly into iot mobile app architecture—auth tokens, message signing, and secure key storage must be part of the plan.
Security and Privacy: Protecting Users, Devices, and Data
IoT raises the stakes: you’re protecting both data and physical systems. Treat security as a first-class feature from day one.
Threat model checklist:
- What an attacker wants: account takeover, device control, data exfiltration, or firmware tampering.
- Attack surfaces: mobile app, BLE pairing, Wi‑Fi provisioning, API endpoints, message broker, cloud storage, OTA pipeline.
Foundational controls:
- Transport security: Enforce TLS 1.2+ for all links; require modern ciphers; apply HSTS and certificate pinning in the app.
- Strong auth: Use OAuth 2.0/OIDC; prefer short-lived tokens with refresh; bind sessions to device fingerprints; support hardware-backed key storage (Secure Enclave/Keystore).
- Device identity: Provision unique credentials per device; rotate keys; sign commands and firmware; verify device certificates.
- Data minimization: Collect only necessary telemetry; redact PII; encrypt sensitive data at rest in the app and cloud.
- Secure storage: Use OS keystores for tokens; encrypt local caches; wipe on logout.
- Secure BLE: Use LE Secure Connections; pair/bond flows with user confirmation; randomize MAC where possible; restrict GATT characteristics.
- Backend hardening: Rate-limit, WAF, input validation, and least-privilege IAM.
Operational readiness:
- Logging: Structured logs with correlation IDs; avoid sensitive payloads.
- Monitoring: Security alerts on anomalies (failed logins, topic floods, firmware mismatch).
- Updates: Signed OTA with rollback; staged rollouts; audit trails.
- Compliance: Map to GDPR/CCPA and industry standards early to avoid costly rework.
Deep dive: Review practical guidance in IoT Security Best Practices for 2025.
Developer enablement:
- Security linters in CI, SAST/DAST, dependency scanning.
- Secrets management: no hard-coded keys; use vaults.
- Red team drills and pen tests pre-launch.
SEO tip: Use headings with security keywords alongside cross platform iot app to capture high-intent traffic.

Backend Services and IoT Mobile App Architecture
Your backend is the backbone of reliability and scale. Aim for a modular iot mobile app architecture that separates ingestion, processing, storage, and APIs.
Core components:
- Device registry: identity, certificates, metadata, and lifecycle.
- Ingestion: MQTT broker or WebSocket/HTTP gateway.
- Rules/stream processing: filter, enrich, route telemetry to storage and alerts.
- Storage: time-series for metrics, object storage for blobs, relational/NoSQL for config.
- Command and control: secure path for downlinks with auditing and idempotency.
- API gateway/GraphQL: unified access for mobile and web.
- Notifications: push and webhooks.
- OTA service: signed firmware distribution and staged rollouts.
Architecture pattern:
- Event-driven design for decoupling.
- Stateless microservices with horizontal scaling.
- Caching for hot reads (device states, dashboards).
- Backpressure and DLQs for resilience.
Platform and data choices:
- Evaluate managed IoT platforms for speed and reliability; see Top 10 IoT Platforms You Should Use in 2025.
- Match data models to access patterns and cost; read Choosing the Right Database for IoT Applications.
Mobile considerations:
- Token-scoped APIs (principle of least privilege).
- Real-time subscriptions with pagination and deltas to reduce payloads.
- Offline sync and conflict resolution.
Deliver an API contract early so your react native iot app or Flutter client can build in parallel and mock responses.
Finally, surface insights beautifully: reference How to Build an IoT Dashboard for data visualization patterns that translate well to mobile.
Testing Across Platforms, Devices, and Networks
Quality hinges on realistic testing across OS versions, device models, and network conditions.
Plan a layered strategy:
- Unit tests: business logic, parsers, reducers, state machines.
- Integration tests: BLE pairing flows, MQTT subscriptions, API interactions.
- End-to-end tests: real devices in lab rigs; simulate sensor input and firmware states.
- Usability tests: observe users handling errors, delays, or confusing states.
Device and OS coverage:
- Maintain a matrix spanning iOS and Android versions, screen sizes, chipsets, and memory profiles.
- Include edge devices with low RAM and older radios.
Network realism:
- Throttle to 2G/3G, add packet loss and high latency.
- Test offline queuing, reconnection strategies, and data reconciliation.
Framework tips:
- React Native: Jest/RTL for UI, Detox for E2E; validate background tasks and headless JS.
- Flutter: widget tests, integration_test, and device labs; profile jank and memory.
Security and privacy tests:
- Token expiry, key rotation, and cert pinning failures.
- Permissions prompts and revocations (Bluetooth, Location, Notifications).
Operational readiness:
- Load test ingestion and APIs before mobile release.
- Chaos drills for broker or database outages.
Document defects with repro steps and device logs so fixes land quickly across your cross platform iot app clients.
Performance and Battery Optimization
Smooth performance and long battery life are table stakes for a cross platform iot app.
General strategies:
- Push over polling: Use MQTT/WebSockets or push notifications to avoid frequent REST polling.
- Batch and compress: Aggregate telemetry and send in bursts; gzip or use binary formats when appropriate.
- Intelligent intervals: Adjust refresh rates based on app state (foreground vs background) and device capability.
- Minimize re-renders: Memoize, debounce, and virtualize long lists.
- Background work: Use OS-specific schedulers; avoid wake-locks unless essential.
React Native specifics:
- Enable Hermes for lower memory and faster startup.
- Use the new architecture (Fabric/TurboModules) for lower bridge overhead.
- Offload heavy work to native threads; avoid large JSON diffs across the bridge.
Flutter specifics:
- Use const widgets and efficient state management to minimize rebuilds.
- Profile with DevTools; fix layout thrash and shader compilation stutter.
- Use isolates for CPU-heavy parsing or crypto.
BLE and radio care:
- Keep scans short; filter by service UUIDs.
- Prefer connection parameter updates and notifications over frequent reads.
Measure continuously: Profile cold start, frame times (FPS), memory, and energy impact. Regressions are easier to catch early than after launch.
Deploying and Maintaining Your IoT App
Deployment touches app stores, device fleets, and your cloud. Aim for safe, repeatable releases.
Store readiness:
- Permissions: Justify Bluetooth, Location, Notifications, and Background modes with clear copy.
- Privacy: Transparent disclosures and opt-ins; allow data export/deletion.
- Review: Provide demo accounts and test devices if required.
Release engineering:
- CI/CD: Automated builds, code signing, and store uploads; snapshot builds for QA.
- Feature flags: Roll out new device controls or dashboards gradually.
- Phased releases: Start with a small percentage and ramp up.
Post-release maintenance:
- Hotfix playbook for critical bugs.
- Compatibility testing for new iOS/Android releases and OEM changes.
- Dependency updates on a predictable cadence.
Customer success:
- In-app diagnostics: export logs, device info, and timestamps.
- Guided troubleshooting: link from errors to knowledge base.
Budgeting: Keep aside runway for ongoing device certifications, lab testing, and localization. For planning, see IoT App Development Cost: Complete Guide.
Monitoring, Analytics, and IoT Dashboards
Observability gives you insight into user experience and device health.
What to measure:
- App health: crashes, ANRs, cold start, memory.
- Engagement: active users, session length, feature adoption.
- Device metrics: online rates, telemetry freshness, command success, firmware rollout progress.
- Alerts: frequency, MTTA/MTTR, false positives.
In-app visibility:
- Telemetry timelines on device detail screens.
- Alert center with filters and trends.
- Usage analytics to refine iot app ui ux design.
Backend visibility:
- Broker metrics (connections, dropped packets, latency).
- Stream processing throughput and lag.
- Database health and query performance.
Dashboards: For layout patterns, KPIs, and data storytelling, see How to Build an IoT Dashboard. Industrial teams can adapt examples from Industrial IoT: Building Remote Monitoring Systems.
Action loops:
- Tie product analytics to A/B tests (e.g., alternative control layouts).
- Feed support tickets into backlog with quant data.
- Align SLOs to customer SLAs and alert on breach risk.
Data governance: Pseudonymize user data for analytics where possible and retain only as long as necessary.
Planning for Scalability and Future Growth
Design for growth from day one so your cross platform iot app scales with users and device fleets.
Scaling patterns:
- Multi-tenant architecture with clear tenant isolation in topics, DB schemas, and IAM.
- Horizontal scale for stateless services; reserved capacity for brokers and databases.
- Backpressure: circuit breakers, queues, and dead-letter topics.
- Topic taxonomy: consistent MQTT topics (tenant/device/type) for routing and least-privilege policies.
Data strategy:
- Hot vs. cold paths: stream aggregates for UI, archive raw data to cheaper storage.
- TTL and tiering: age out noisy telemetry; precompute dashboards to cut p95 latency.
- Reindexing plan: schema evolution without downtime.
Mobile future-proofing:
- Config-driven UI for new device types without forced updates.
- Remote feature flags for progressive capabilities.
- Compatibility shims for older OSes and devices.
Ecosystem choices:
- Periodically reassess managed IoT platforms and DB engines as needs evolve: Top 10 IoT Platforms You Should Use in 2025 and Choosing the Right Database for IoT Applications.
Resilience drills:
- Broker failover tests, regional evacuations, and OTA rollback simulations.
- Load testing for big events (e.g., mass firmware update or daylight savings scene triggers).
With a strong iot mobile app architecture, adding device families, geographies, and advanced analytics becomes incremental rather than disruptive.
Looking for an IoT app development partner?
Are you looking for a reliable partner to help you build a stunning IoT companion app? You're in the right place.
We have 6+ years of experience building a variety of IoT apps, from healthcare to HVAC. So, if you go with us, you'll be in safe hands.
If you want to learn more, feel free to reach out and our team will be happy to set up a call to discuss your needs in more detail.
Get in touch